|
You
are here: /main/research
expeditions/May 2005/Unnamed Seamount
Mapping
an Unnamed Seamount SE of Pearl and Hermes Atoll
By Jonathan
R. Weiss
Seafloor Mapping Specialist
NOAA Coral Reef Ecosystem Division
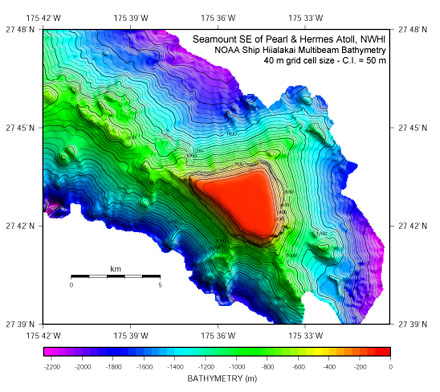
Multi-beam
mapping aboard the NOAA Ship Hiialakai during the recent coral
bleaching Cruise in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands (NWHI)
has enabled NOAA scientists to create images of the seafloor
such as these, in locations where little data were previously
available. For example, prior to the cruise, the seamount
in these images, located southeast of Pearl and Hermes Atoll,
NWHI, was unmapped and only one forty fathom (-73 m) sounding
existed in its vicinity.
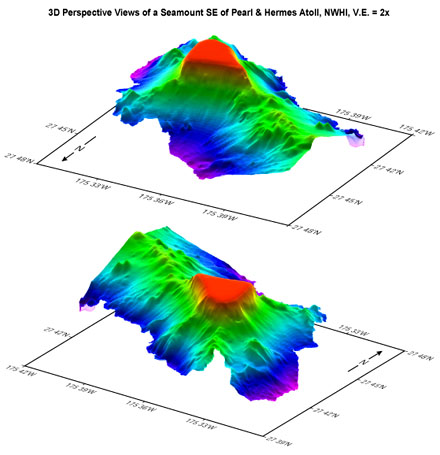
There
is over 2000 m of relief between the top of the seamount at
-105 m and the surrounding seafloor. The northwest-trending
ridge connecting the seamount to Pearl and Hermes atoll suggests
a linked geologic history between the two submarine mountains.
The small peaks on top of the ridge might suggest the presence
of ancient volcanic centers and the hummocky topography on
the north face of the ridge may be slump blocks. Additional
linear ridges radiate from the northern and southwestern apices
of the triangular-shaped seamount in a fashion similar to
submarine volcanic rift zones such as the southeast rift zone
of the active Kilauea Volcano on Hawaii Island. The flat-topped
nature of the seamount suggests it was planed off by erosion
at sea level tens of millions of year ago and has since subsided
to its present depth as the Pacific tectonic plate moves to
the northwest.
In addition
to the geologic significance of the data, it is of biological
and resource management importance as well. For example, the
location of the newly mapped seamount is associated with monk
seal foraging sites, and the data around Pearl and Hermes
Atoll will aid in NWHI Coral Reef Ecosystem Reserve boundary
determination. This is just one of many exciting new pieces
of information gained through the combined efforts of NOAA’s
National Marine Sanctuary Program and Coral Reef Ecosystem
Division.
|